Imagine a lush garden that doesn’t just look beautiful but also helps manage stormwater and prevent flooding in your yard. Sounds idyllic, right? Welcome to the world of rain gardens—a sustainable solution for homeowners and garden enthusiasts looking to transform their outdoor spaces while addressing water drainage issues, perfect solution now that we’re heading into autumn.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the many benefits of rain gardens, offer practical tips for designing your own, and discuss how they play a crucial role in sustainable water management. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or a homeowner dealing with soggy lawns, this post will provide you with all the information you need to get started.
What is a Rain Garden?
A rain garden is a specially designed, shallow depression planted with native vegetation that collects and absorbs rainwater runoff from impervious surfaces like roofs, driveways, and pavement. Unlike traditional gardens, rain gardens are engineered to manage stormwater naturally, reducing the risk of flooding and erosion.
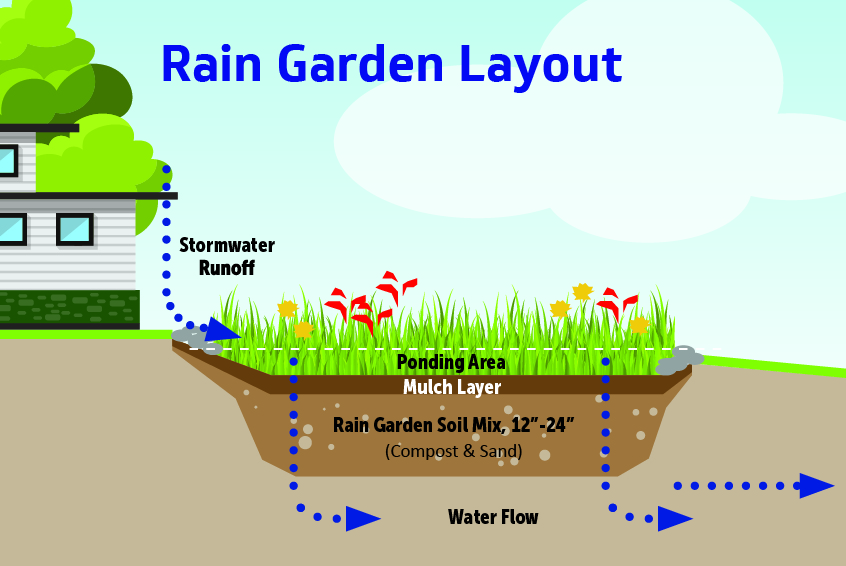
The Science Behind Rain Gardens
Rain gardens work by capturing and slowing down stormwater runoff, allowing it to percolate into the ground rather than rushing into storm drains. This process not only prevents flooding but also filters pollutants from the water, improving the quality of local waterways.
Benefits for Your Yard
Creating a rain garden in your yard offers numerous advantages. It not only helps manage excess water but also enhances the aesthetic appeal of your garden. With the right plants, a rain garden can become a vibrant habitat for birds and pollinators, adding biodiversity to your back garden.
Why You Need a Rain Garden
Flooded gardens can be a homeowner’s nightmare, leading to waterlogged plants, soil erosion, and even structural damage to your property. A rain garden provides a natural and effective solution to these problems, transforming your garden into a functional and attractive landscape.
Cost-Effective and Eco-Friendly
Rain gardens are a cost-effective solution for managing stormwater. They reduce the need for expensive drainage systems and lower your water bills by promoting natural filtration and groundwater recharge. Plus, they contribute to a healthier environment by reducing surface runoff and preventing water pollution.
Enhancing Curb Appeal
A well-designed rain garden can significantly boost your home’s curb appeal. With a variety of colourful native plants, you can create a visually striking garden that stands out in your neighbourhood. It’s not just about functionality; it’s about creating a space that you and your neighbours can admire.
Supporting Local Wildlife
By planting native species, you provide a habitat for local wildlife, including birds, bees, and butterflies. Rain gardens are a great way to support biodiversity and contribute to the overall health of your local ecosystem.

Designing Your Rain Garden
Designing a rain garden involves careful planning and consideration of several factors, including location, size, soil type, and plant selection. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started.
Choosing the Right Location
The ideal location for a rain garden is a low-lying area that naturally collects water. It should be at least 10 feet away from your home’s foundation to prevent water from seeping into your basement. Avoid areas with poor drainage or heavy clay soils, as these can hinder water absorption.
Determining the Size
The size of your rain garden depends on the amount of runoff you need to manage. A general rule of thumb is to make your rain garden about one-third the size of the area draining into it. Use a measuring tape to calculate the dimensions, and mark the outline with stakes and string.
Soil Preparation
Good soil is the key to a successful rain garden. Most rain gardens require a mix of sand, compost, and existing soil to ensure proper drainage. You may need to amend your soil by adding organic matter to improve its structure and water-holding capacity.
Selecting Plants for Your Rain Garden
Choosing the right plants is crucial for the functionality and beauty of your rain garden. Native plants are typically the best choice, as they are adapted to your local climate and require less maintenance.

Installing Your Rain Garden
Once you’ve planned and prepared your rain garden, it’s time to start digging. Follow these steps to ensure a successful installation.
Excavation and Shaping
Dig out the area to the desired depth, usually between 6 to 12 inches. Create a gentle slope from the edges to the centre to encourage water flow. Use the excavated soil to build a berm on the downhill side of the garden to hold water in.
Adding Soil Amendments
Mix the excavated soil with sand and compost to create a well-draining soil mixture. Spread this mixture evenly across the garden bed, ensuring a uniform depth. Rake the surface smooth and level.
Planting and Mulching
Place your plants in the garden according to your design plan. Dig holes twice as wide as the root ball and deep enough to cover the roots. Backfill with soil and firm gently. Apply a 2-3 inch layer of mulch to retain moisture and suppress weeds.
Maintaining Your Rain Garden
Maintenance is essential to keep your rain garden healthy and functioning properly. Regular care will ensure that it continues to manage rain water effectively and remains an attractive feature in your yard.
Watering and Weeding
Water your rain garden regularly during the first growing season to help establish the plants. Once established, native plants typically require less watering. Weed the garden periodically to prevent invasive species from taking over.
Pruning and Deadheading
Prune dead or damaged plant material to maintain a neat appearance. Deadhead spent flowers to encourage new blooms and prevent self-seeding. In late winter, cut back perennials and grasses to make way for new growth.
Monitoring and Adjusting
Keep an eye on your rain garden’s performance during heavy rains. If you notice standing water or erosion, adjust the soil or plant placement to improve drainage. Add more mulch as needed to maintain a protective layer.

Conclusion
Rain gardens are a beautiful and practical solution for managing stormwater and preventing flooding in your yard. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can create a rain garden that not only enhances your landscape but also contributes to a healthier environment.
Ready to get started on your rain garden project? Join our community of garden enthusiasts and share your experiences. And if you need expert advice, don’t hesitate to reach out to our team. Happy gardening!
